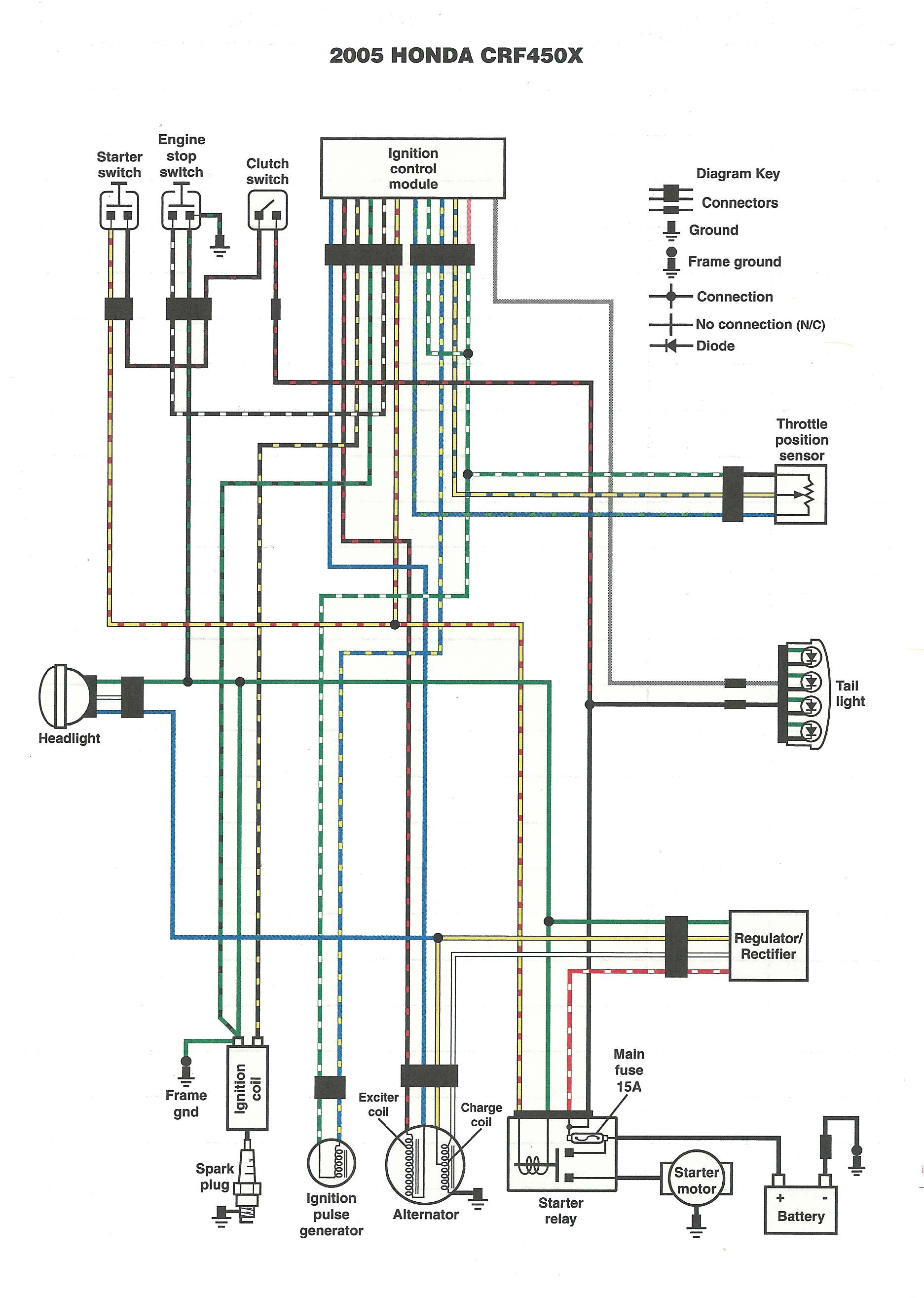
Motorcycle Ignition Wiring Diagram is a crucial tool for any motorcycle mechanic or enthusiast working on their bike’s electrical system. Understanding how to read and interpret these diagrams can help you troubleshoot electrical issues and make necessary repairs with ease.
Why are Motorcycle Ignition Wiring Diagrams essential?
Motorcycle Ignition Wiring Diagrams are essential for several reasons:
- They provide a visual representation of the electrical system, showing how various components are connected.
- They help identify the location of key components such as the ignition switch, starter relay, and spark plugs.
- They assist in diagnosing electrical problems and tracing wiring issues.
How to read and interpret Motorcycle Ignition Wiring Diagrams effectively
Reading and interpreting Motorcycle Ignition Wiring Diagrams may seem daunting at first, but with a little practice, you can easily decipher them:
- Start by familiarizing yourself with the symbols and color codes used in the diagram.
- Identify the key components and follow the flow of the electrical system from the battery to the ignition system.
- Pay attention to the connections and wiring routes to understand how electricity flows through the system.
Using Motorcycle Ignition Wiring Diagrams for troubleshooting electrical problems
Motorcycle Ignition Wiring Diagrams are invaluable tools for troubleshooting electrical issues on your bike:
- Use the diagram to identify potential problem areas such as faulty connections, broken wires, or malfunctioning components.
- Follow the wiring diagram to trace the source of the problem and make necessary repairs or replacements.
- Refer to the diagram to ensure proper reassembly and connection of components after troubleshooting.
Safety precautions when working with electrical systems
Working with motorcycle electrical systems can be dangerous if proper precautions are not taken. Here are some safety tips to keep in mind:
- Always disconnect the battery before working on the electrical system to prevent electrical shock or short circuits.
- Avoid working on the electrical system in wet or damp conditions to reduce the risk of electrical hazards.
- Use insulated tools and wear protective gear such as gloves and goggles when handling electrical components.
Motorcycle Ignition Wiring Diagram
Ignition Simple Motorcycle Wiring Diagram

Step-by-Step Guide: How to Wire a Motorcycle Ignition Switch: Wiring

honda motorcycle ignition wiring diagram
Basic Wiring Motorcycle Wiring Diagrams

Ignition Diagram Motorcycle

Basic Wiring Diagrams For Motorcycles