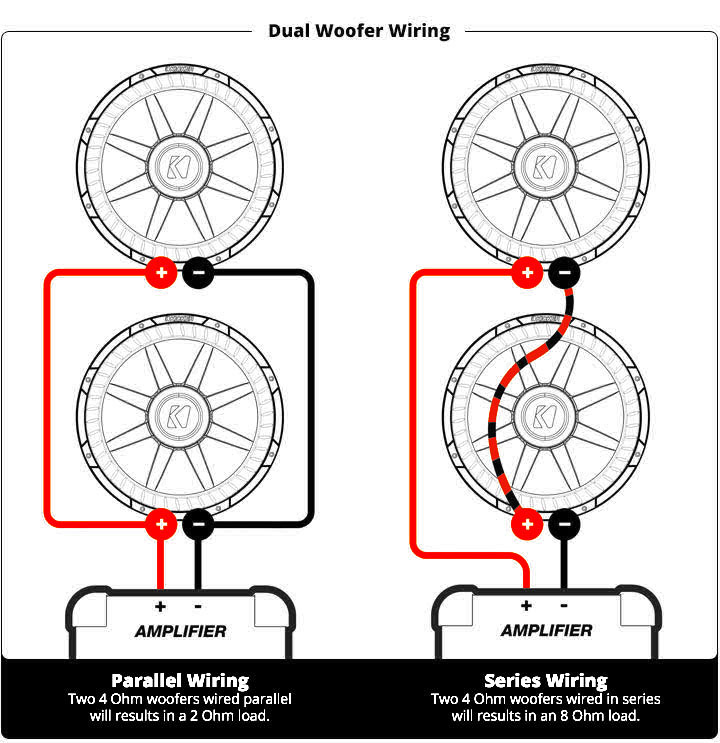
Parallel Sub Wiring is a crucial aspect of setting up a car audio system. It involves connecting multiple subwoofers to a single amplifier by running multiple wires from the positive terminal of the amp to the positive terminal of each subwoofer, and from the negative terminal of the amp to the negative terminal of each subwoofer. This setup allows each subwoofer to receive the same amount of power from the amplifier, resulting in a balanced and powerful sound output.
Why Parallel Sub Wiring is Essential
Parallel Sub Wiring is essential for several reasons:
- It allows you to connect multiple subwoofers to a single amplifier, maximizing the power output.
- It ensures that each subwoofer receives the same amount of power, preventing any imbalance in sound quality.
- It simplifies the wiring setup, making it easier to install and troubleshoot your car audio system.
Reading and Interpreting Parallel Sub Wiring
When reading and interpreting Parallel Sub Wiring diagrams, it is important to understand the following:
- Identify the positive and negative terminals of the amplifier and each subwoofer.
- Follow the wiring diagram carefully to ensure that each subwoofer is connected in parallel to the amplifier.
- Use the appropriate gauge of wire to handle the power output of your amplifier and prevent overheating.
Using Parallel Sub Wiring for Troubleshooting Electrical Problems
Parallel Sub Wiring can be used for troubleshooting electrical problems in your car audio system. By checking the wiring connections of each subwoofer to the amplifier, you can identify any loose or damaged wires that may be causing issues with the sound output. Additionally, you can use a multimeter to test the continuity of the wires and ensure that they are properly connected.
Importance of Safety
Working with electrical systems and wiring diagrams can be dangerous if proper precautions are not taken. Here are some safety tips and best practices to keep in mind:
- Always disconnect the power source before working on any electrical components.
- Use insulated tools to prevent electric shocks.
- Avoid working in wet or damp conditions to prevent the risk of electric shock.
- Double-check all connections before powering on the system to prevent short circuits.
Parallel Sub Wiring
Wiring Subwoofer In Parallel

2 ohm subwoofer parallel wiring diagram
[47+] Parallel Circuit Wiring Diagram, Wiring Diagrams For Electrical
![Parallel Sub Wiring [47+] Parallel Circuit Wiring Diagram, Wiring Diagrams For Electrical](https://i1.wp.com/blog.sonicelectronix.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/parallel-768x1651.jpg)
Amp And Speaker Wiring Kit

Series and Parallel Subwoofer Wiring – Blog | Sonic Electronix

Wiring Subwoofer In Parallel
